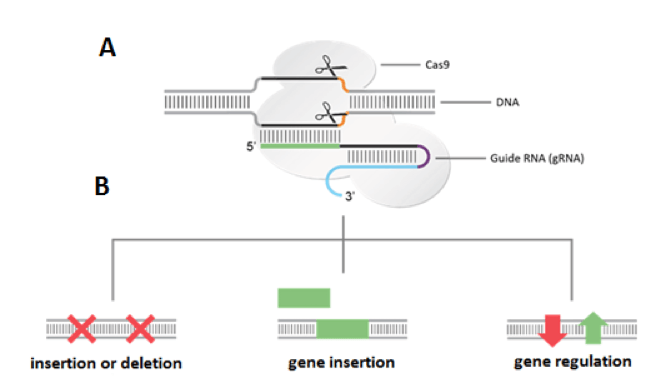
T (G12V) mutant allele (Supplementary Table 1)The importance of the seed region and PAM motif has been studied using a few spacers in Type IE CRISPR system in E coli K12 However, it is unknown whether spacer sequence has an effect on the activities of CRISPR system We have analyzed CRISPR interference and priming using 18 endogenous spacers in E coli K12 to reexamine the PAM and seedThe popularity of CRISPR is largely due to its simplicity As shown in Figure 1, the CRISPRCas system relies on two main components a guide RNA (gRNA) and CRISPRassociated (Cas) nuclease The guide RNA is a specific RNA sequence that recognizes the target DNA region of interest and directs the Cas nuclease there for editing
Researchers Employing Crispr For Soybean Advancement Research Highlight Soybean Research Information Network Srin
Crispr seed region
Crispr seed region-The clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)associated enzyme Cas9 is an RNAguided nuclease that has been widely adapted for genome editing in eukaryotic cells However, the in vivo target specificity of Cas9 is poorly understood and most studies rely on in silico predicti The clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)An example of embryoseed fluorescence reporter/clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)associated protein 9 (EmSFR/Cas9) designed to target Zmd (A) Images of the same maize ear (from Event #PT434) carrying EmSFR/Cas9 under brightfield (left panel) and upon excitation of red fluorescence (right) using an




Researchers Employing Crispr For Soybean Advancement Research Highlight Soybean Research Information Network Srin
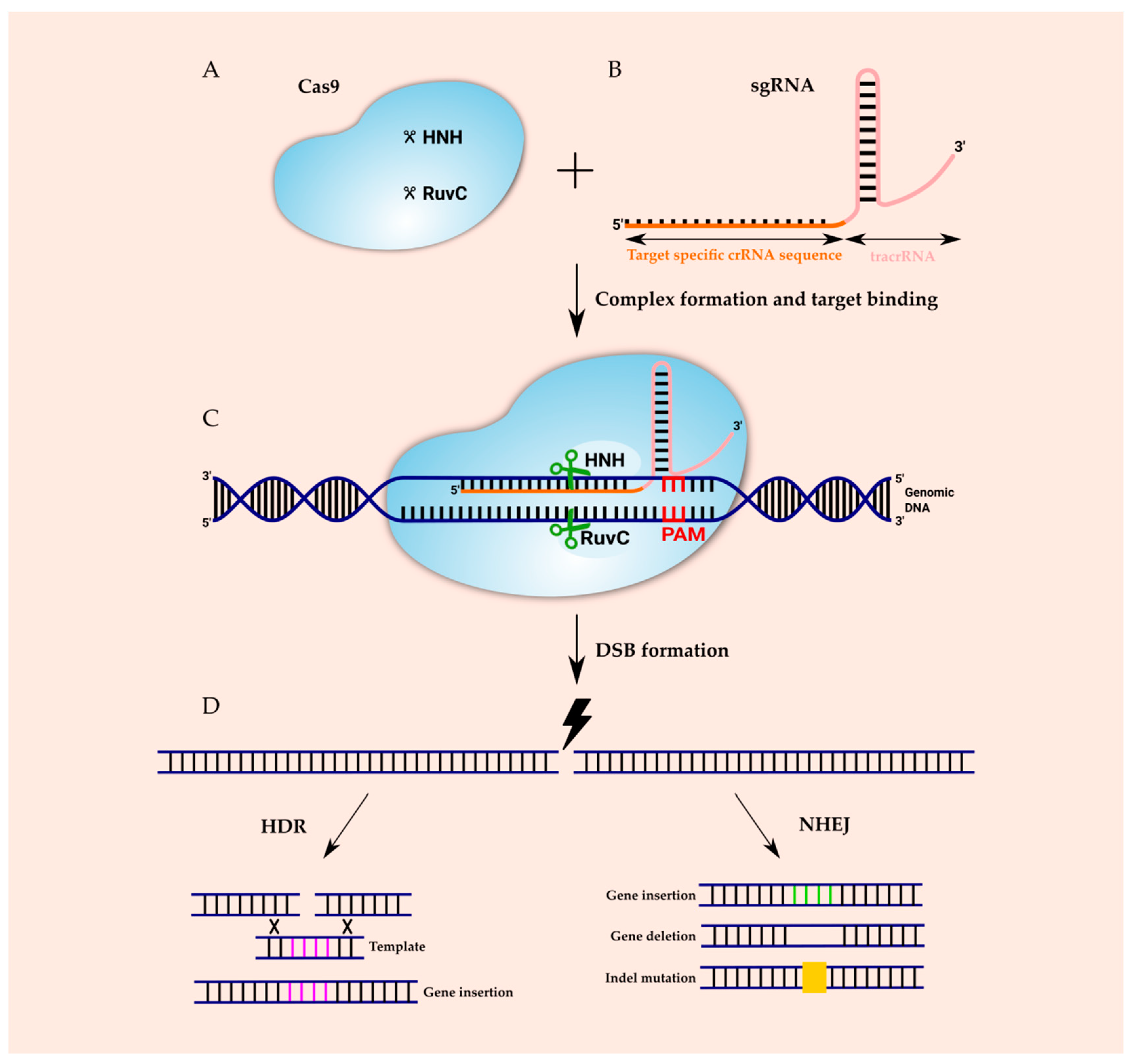
CRISPR is a remarkably flexible tool for genome manipulation, since Cas enzymes bind target DNA independently of their ability to cleave target DNA Specifically, both RuvC and HNH nuclease domains can be rendered inactive by point mutations (D10A and H840A in SpCas9), resulting in a nuclease dead Cas9 (dCas9) molecule that cannot cleave target DNACRISPRCas adaptive immunity in bacteria and archaea uses RNAguided nucleases to target and degrade foreign nucleic acids (1–3)The CRISPRCas9 family of proteins has been widely deployed for gene editing applications (4, 5) based on the precision of doublestranded DNA (dsDNA) cleavage induced by two catalytic domains, RuvC and HNH, at sequencesCRISPR/Cas9 is a versatile genomeediting technology that is widely used for studying the functionality of genetic elements, creating genetically modified organisms as well as preclinical research of genetic disorders However, the high frequency of offtarget activity (≥50%)—RGEN (RNAguided endonuclease)induced mutations at sites other than the intended
Using thousands of guide RNAs with 1, 2 or 3 singleletter mismatches to their target RNA, they identified a critical seed region that is exquisitely sensitive to mismatches between the CRISPRStep 1 Provide an RNA sequence to target Input an RNA/cDNA sequence that users want to target in FASTA format into the Step 2 Choose the reference transcriptome Select a reference transcriptome from the dropdown menu custom Users can Step 3 Describe the PFS and crRNA requirements PFSTechnology and to investigate the function of a specific miRNA, we used CRISPR/Cas9 to deplete human miR93 from a cluster by targeting its 5' region in HeLa cells Various small indels were induced in the targeted region containing the Drosha processing site and seed sequences Interestingly, we found that even a single nucleotide deletion
Dr Eyal Emmanuel, Chairman of the CRISPRIL consortium and VP New Directions of Evogene, commented, We are delighted to be continuing our important research in one of the forefront areas of innovation – the merge of computational power and genetics The approval of the second period of the consortium by the IIA is a vote of confidence inThe effect of a single mismatch is more pronounced for mismatches far away from the PAM site (PAMdistal region) as opposed to PAMproximal nucleotides, sometimes referred to as the seed region Mismatch tolerance appears to be maximal at the th position This suggests that guides should be carefully designed to avoid mismatch at that positionOr (2) Near PAM located within the spacer region, especially the seed region of short guide RNAs (sgRNAs) 3, 4



Crispr Cpf1 Proteins Structure Function And Implications For Genome Editing Cell Bioscience Full Text




A Review Of Crispr Associated Genome Engineering Application Advances And Future Prospects Of Genome Targeting Tool For Crop Improvement Springerlink
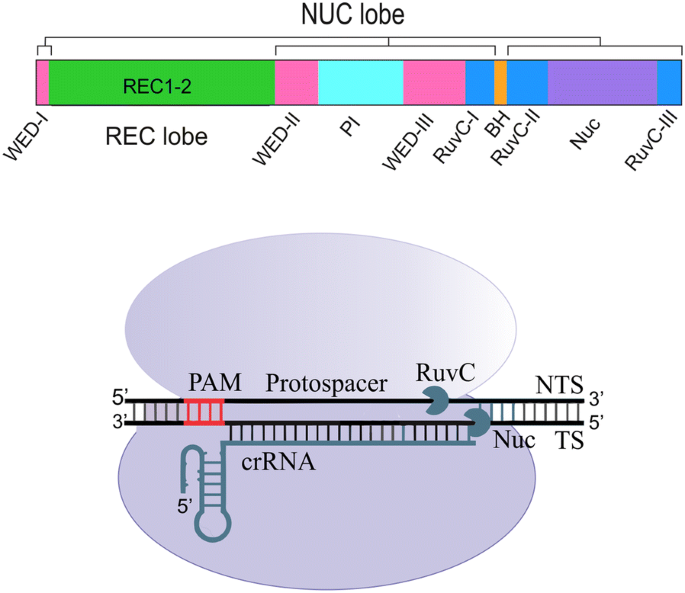
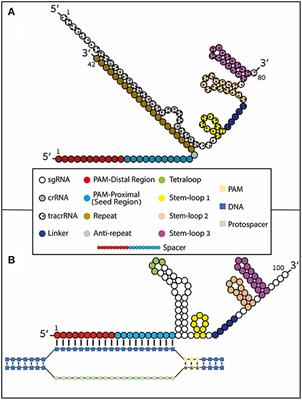
The CRISPRCas9 system has recently evolved as a powerful mutagenic tool for targeted genome editing The impeccable functioning of the system depends on the optimal design of single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) that mainly involves sgRNA specificity and ontarget cleavage efficacy Several research groups have designed algorithms and models, trained on mammalianColi subtype CRISPR/Cas system, the requirements for crRNA match ing are strict only for a sevennucleotide seed region of a protospa cer immediately following the essential protospaceradjacent motif Mutations in the seed region abolish CRISPR/Cas mediated immunity by reducing the binding affinity of the crRNAguided Cascade complex toThe CRISPRCas system is widely found in bacterial and archaeal genomes as a defense mechanism against invading viruses and plasmids 1–6 The type II CRISPRCas system from Streptococcus pyogenes relies on only one protein, the nuclease Cas9, and two noncoding RNAs, crRNA and tracrRNA, to target DNA These two noncoding RNAs can further be fused into one




Origins And Evolution Of Crispr Cas Systems Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society B Biological Sciences



Iopscience Iop Org
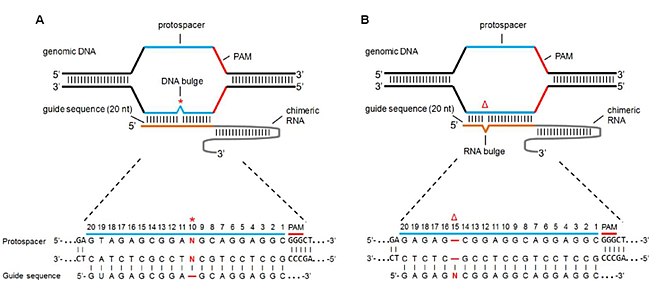
Premium Mirai85 seed samples, 15seeds ×2 varieties, 30 kernes in totalThe PS2– and PS3–gRNA seeds region ( and 22 nt, respectively) were predicted to pair with the coding strand of OsMPK5, and PS3–gRNA would guide Cas9 to make DSB at a SacI site (Figure 2B) Subsequently, three gRNA–Cas9 constructs were made by inserting the synthetic DNA oligonucleotides which encode the gRNA seed into the pRG vectorWithin predicted offtargets, nucleotide mismatches affecting annealing of the socalled 'seed region' of the guide RNA (8–12 nt at the 3′ end of the nt guide sequence in the case of Cas9) lower CRISPR/Cas activity significantly more than mismatches positioned towards the 5′ end of the bp DNA target (Hsu et al 13)
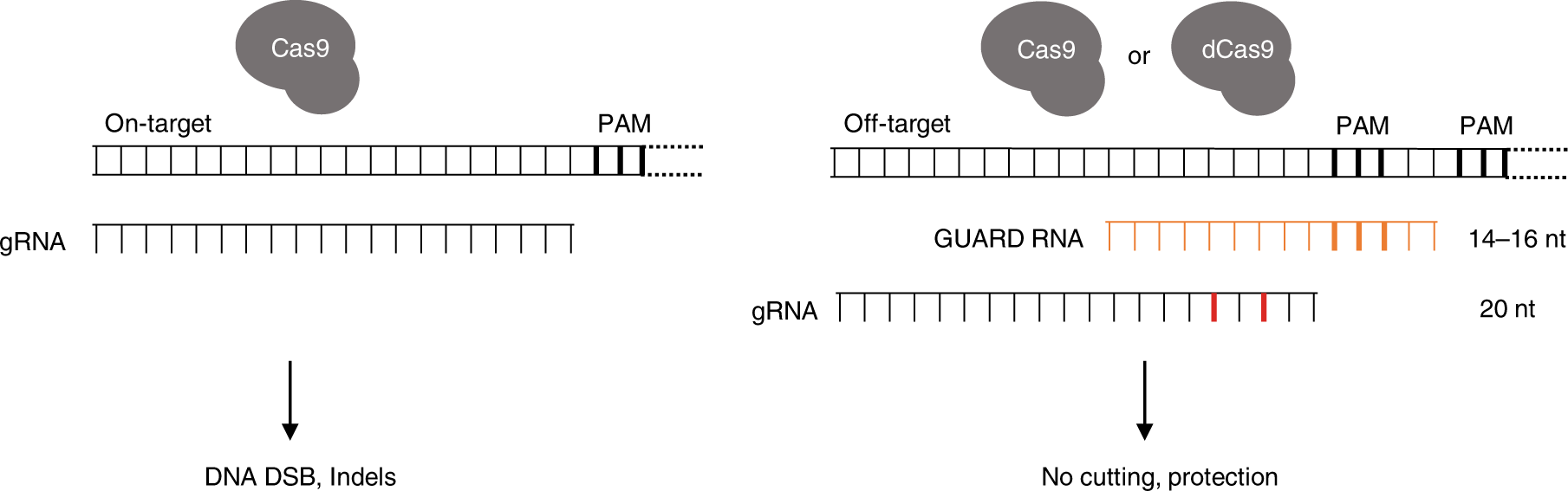



Crispr Guard Protects Off Target Sites From Cas9 Nuclease Activity Using Short Guide Rnas Nature Communications




Crispr Cas9 Abm Inc
The spacer segment, which is complementary to the target DNA, contains a seed region with eight nucleotides length Seed region flanks at the initial part of the spacer and plays a notable role in the target specificity of CRISPR–Cpf1 system (Fig 3)Crispr seed regionWhen a mismatch is intr oduced intoCRISPRDT (CRISPR DNA Targeting) is a web application to help biologists design optimal gRNAs for the CRISPRCpf1 system CRISPRDT is essentially composed of many interfaces and a backend pipeline Maximum number of mismatches and gaps in seed region tolerated by off targets The seed region stands for 6 nucleotides in theMismatches between the target and CRISPR RNA guide outside the seed have minor effects on target binding, thus contributing to offtarget activity of CRISPRCas effectors tospacer region



Off Target Genome Editing Wikipedia




Crispr Cas9 System A Bacterial Tailor For Genomic Engineering
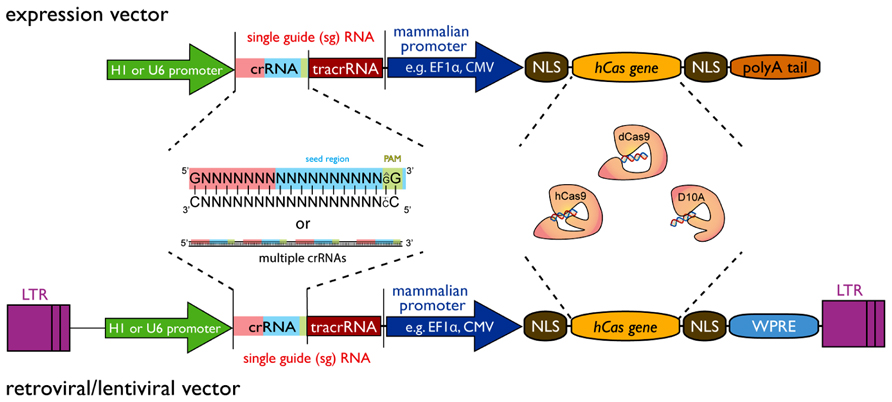
The clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)/CRISPRassociated nuclease 9 (Cas9) genome editing technology provides such a tool, enabling revolutionary advances in both arenas of plant biology CRISPR/Cas systems are bacterial adaptable immune systems against foreign DNA sources such as bacteriophages or plasmids ( WiedenheftAll gRNAs containing UUUU in the guide sequence had been preselected for exclusion from our analysis Furthermore, recent work suggested that three repetitive uracils (UUU) in the seed region of the guide sequence could be responsible for decreased CRISPR activity Thus, a more stringent assessment was applied to evaluate the impact of potential transcription endingTarget recognition by Cas9 requires both a seed sequence in the crRNA and a GG dinucleotidecontaining PAM sequence adjacent to the crRNAbinding region in the DNA target We further show that the Cas9 endonuclease can be programmed with guide RNA engineered as a single transcript to target and cleave any dsDNA sequence of interest
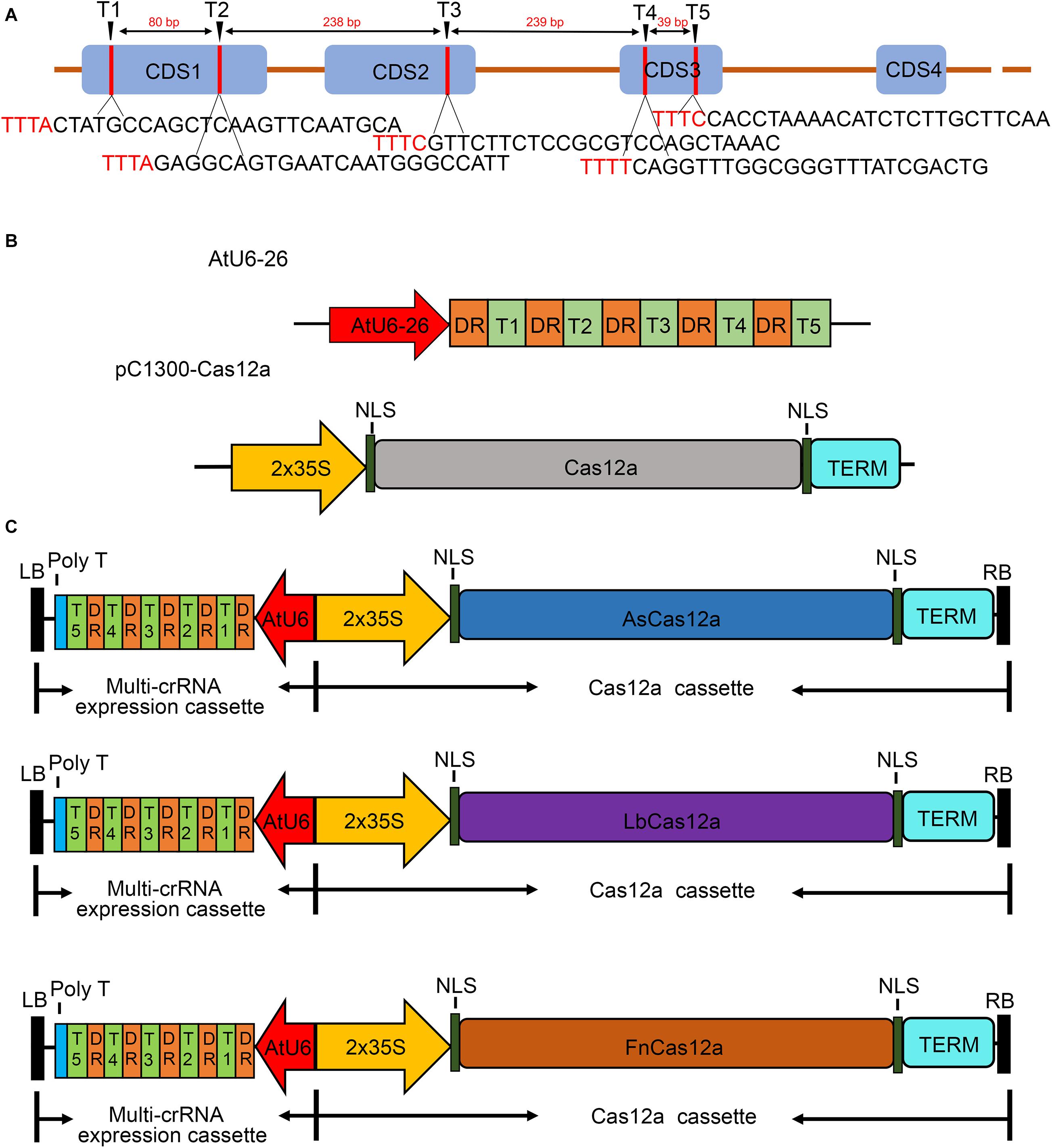



Frontiers Efficient Genome Editing In Populus Using Crispr Cas12a Plant Science
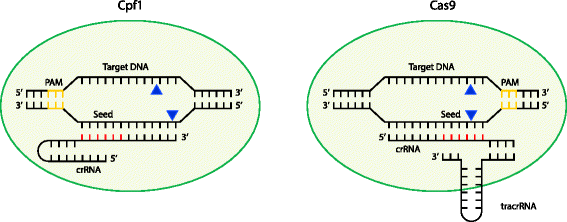



The Cpf1 Crispr Cas Protein Expands Genome Editing Tools Genome Biology Full Text
Selective targeting of KRAS c35 G >CRISPR system provides a highly specific genome editing that is capable of discriminating diseasecausing alleles from wildtype ones, whenever the genetic variants (1) In PAM generate unique protospacer adjacent motifs (PAMs);Adapted from Ran AF et al Double nicking by RNAguided CRISPR Cas9 for enhanced genome editing specificity Cell (13) Enhancing Specificity with Modified Nucleases 5' 3' 3' 5' gRNA 2 gRNA 1 dCas9 Fok1 Fok1 Adapted from Tsai SQ et al Dimeric CRISPR RNAguided FokI nucleases for highly specific genome editing Nat




Crispr Diagnosis And Therapeutics With Single Base Pair Precision Trends In Molecular Medicine




Off Target Genome Editing Wikipedia
One or two mismatches in the seed can be tolerated for CRISPR activity (A) Seed libraries tested in this study The crRNA seed sequence and corresponding region of the nontarget strand of theAbstract Target binding by CRISPRCas ribonucleoprotein effectors is initiated by the recognition of doublestranded PAM motifs by the Cas protein moiety followed by destabilization, localized melting, and interrogation of the target by the guide part of CRISPR RNA moiety The latter process depends on seed sequences, parts of the target that must be strictly complementary to CRISPRMutations in the seed region abolish CRISPR/Cas mediated immunity by reducing the binding affinity of the crRNAguided Cascade complex to protospacer DNA We propose that the crRNA seed sequence plays a role in the initial scanning of invader DNA for a match, before base pairing of the fulllength spacer occurs, which may enhance the
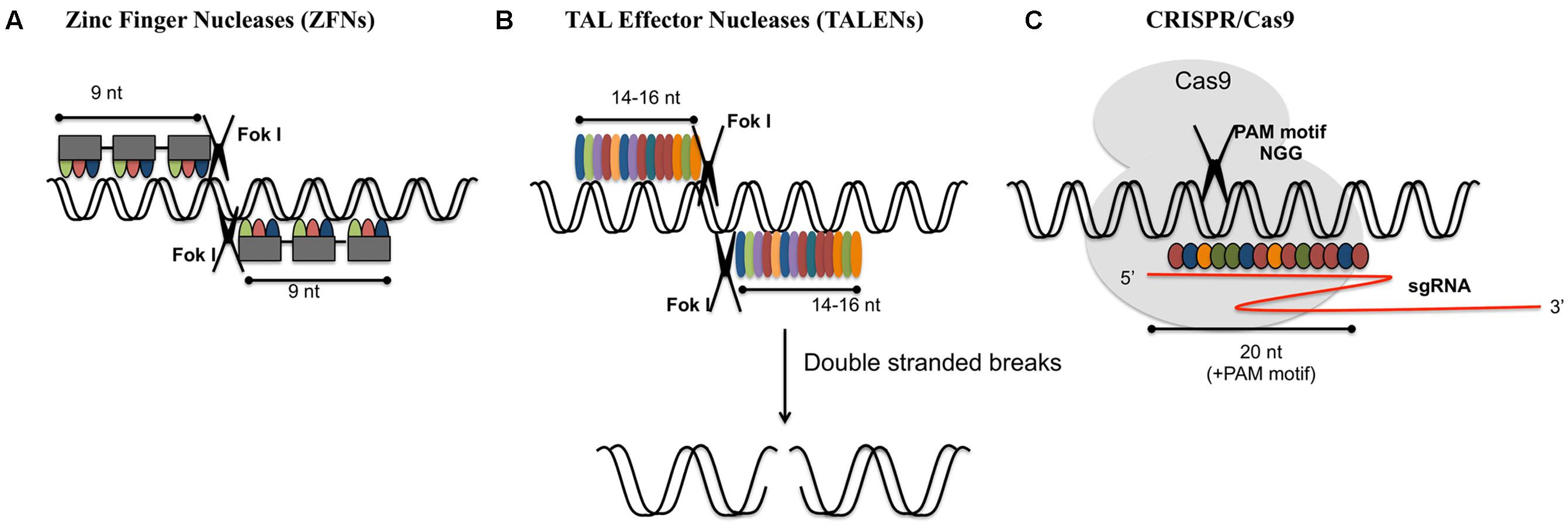



Frontiers Gene Editing And Crop Improvement Using Crispr Cas9 System Plant Science



Overview Of Crispr Cas9 Systems Duke Viral Vector Core
Guide CRISPRassociated (Cas) proteins to cleave foreign nucleic acids1–5 To target particular genomic loci in eukaryotic cells, the type II CRISPRCas system from Our data reveal a welldefined seed region for target binding and a very large number of offtarget binding sites, most of which do not seem to undergo substantialWiedenheft, 13) and the seed region is first used to search for perfect matches and then extended to tolerate mismatches in repeat detection, a shorter seed region can enhance search sensitivity and allow more CRISPR candidates bearing mismatches detectedYou can easily access the CRISPRPLANT v2 data set in three simple steps We made this distinction because different studies suggest slightly different lengths for the SpCas9 seed region Having A and B group spacers allows the user to decide for a more conservative approach with a 10 nt seed for group A In the last step, groups A and B




Off Target Effects In Crispr Cas9 Mediated Genome Engineering Sciencedirect
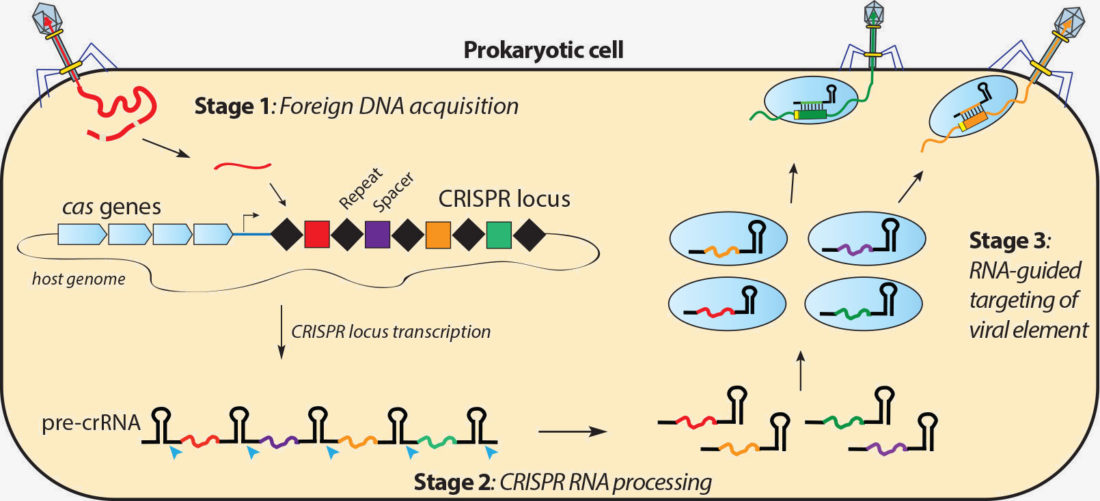



Crispr Systems Doudna Lab
Cific DNA binding A common feature of CRISPRCas systems and other RNAdirected enzymes is that the targeting RNA includes a ''seed'' region The seed region, which, for CRISPRCas enzymes, is a subset of nucleotides within the crRNA that base pairs with PAMproximal nucleotides, is highly sensitiveCRISPRCas9 is quickly revolutionizing the way we approach gene therapy CRISPRCas9 is a complexed, twocomponent system using a short guide RNA (gRNA) sequence to direct the Cas9 endonuclease to the target site Modifying the gRNA independent of the Cas9 protein confers ease and flexibility to improve the CRISPRCas9 system as a genomeediting tool gRNAs have beenCasFinder Guide RNA design for the CRISPR/Cas9 system Genome Mp JGI 31 MpTak1 v51 Search conditions Length of gRNA 18 nt, Seed Region 9 nt, Primary/secondary PAM NGG/NAG Length of gRNA nt, Seed Region 8 nt, Primary/secondary PAM NGG/NAG Enter your sequence (s) in FASTA format below (Please make your sequence as short as



Frontiers Using Synthetically Engineered Guide Rnas To Enhance Crispr Genome Editing Systems In Mammalian Cells Genome Editing



Frontiers A Crispr Case For High Throughput Silencing Genetics
The protospacer adjacent motif (or PAM for short) is a short DNA sequence (usually 26 base pairs in length) that follows the DNA region targeted for cleavage by the CRISPR system, such as CRISPRCas9 The PAM is required for a Cas nuclease to cut and is generally found 34 nucleotides downstream from the cut siteAlthough the CRISPR/Cas9/sgRNA system efficiently cleaves intracellular DNA at desired target sites, major concerns remain on potential "offtarget" cleavage that may occur throughout the whole genome In order to improve CRISPRCas9 specificity for targeted genome editing and transcriptional control, we describe a bioinformatics tool "sgRNAcas9", which is aAn escape phenotype (Fig 1B and Fig S2B), indicating that per fect base pairing of only this part of crRNA (denoted "seed sequence") with the corresponding part of the protospacer (denoted "seed region") as well as an intact PAM sequence are required for interference by the E coli subtype CRISPR/ Cas system



Frontiers Data Mining By Pluralistic Approach On Crispr Gene Editing In Plants Plant Science




Seed Mutations Do Not Completely Block Crispr Interference A Crisprs Download Scientific Diagram
T by CRISPR/Cas9 in CRC cell lines We selected two CRC cell lines, SW6 and SW480, containing the KRAS c35 G >Physical model shows CRISPR/Argonaute offtargeting rules to be kinetic in origin • Seed region and mismatchpattern dependence is due to the kinetics of hybridization • Binding is more promiscuous than cleavage due to kinetically stalled hybridization • Engineered systems can increase specificity without losing ontarget efficiencyThe clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)/CRISPR associated protein (Cas) system, an adaptive immune system found in many archaea and bacteria, has recently emerged




Single Base Resolution Increasing The Specificity Of The Crispr Cas System In Gene Editing Molecular Therapy




Crispr Cas9 Cas12a Biotechnology And Application In Bacteria Sciencedirect
CRISPR (/ ˈ k r ɪ s p ər /) (an acronym for clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) is a family of DNA sequences found in the genomes of prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria and archaea These sequences are derived from DNA fragments of bacteriophages that had previously infected the prokaryote They are used to detect and destroy DNA from similar bacteriophagesSince the repeat sequences of CRISPR arrays could contain mismatches (Sorek, Lawrence &Step 2 Upload the custom reference transcriptome Give a name of the reference transcriptome Upload the reference transcriptome in FASTA format (Note the maximum allowed size for the uploaded transcriptome is 8MIf you want to add a bigger reference transcriptome, please email us and we will add for you




Synthetic Crispr Rna Cas9 Guided Genome Editing In Human Cells Pnas




Genome Modification By Crispr Cas9 Ma 14 The Febs Journal Wiley Online Library
Sale of first CRISPRCas9 gene edited tomato seedlings begins in Japan Japan Bonus 2 Free Sample Hybrid Sweet Corn Seed Sample You will receive Dolce Dream &CRISPRCas9 can be engineered more easily and with less time consumption than ZFNs and TALENs, and it also is highly efficient for highthroughput multiplex genome mismatches between the seed region and its complementary spacer sequence decrease target DNA binding affinity, which is important for effective gene regulationMutations in the seed region abolish CRISPR/Cas mediated immunity by reducing the binding affinity of the crRNAguided Cascade complex to protospacer DNA We propose that the crRNA seed sequence plays a role in the initial scanning of invader DNA for a match, before base pairing of the fulllength spacer occurs, which may enhance the protospacer locating efficiency




Interference By Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat Crispr Rna Is Governed By A Seed Sequence Pnas




The Complete Guide To Understanding Crispr Sgrna
Many bacterial clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)–CRISPRassociated (Cas) systems employ the dual RNA–guided DNA endonuclease Cas9 to defend against invading phages and conjugative plasmids by introducing sitespecific doublestranded breaks in target DNA Target recognition strictly requires the presence of a short protospacer adjacent



Academic Oup Com



Ijms Free Full Text Various Aspects Of A Gene Editing System Crispr Cas9
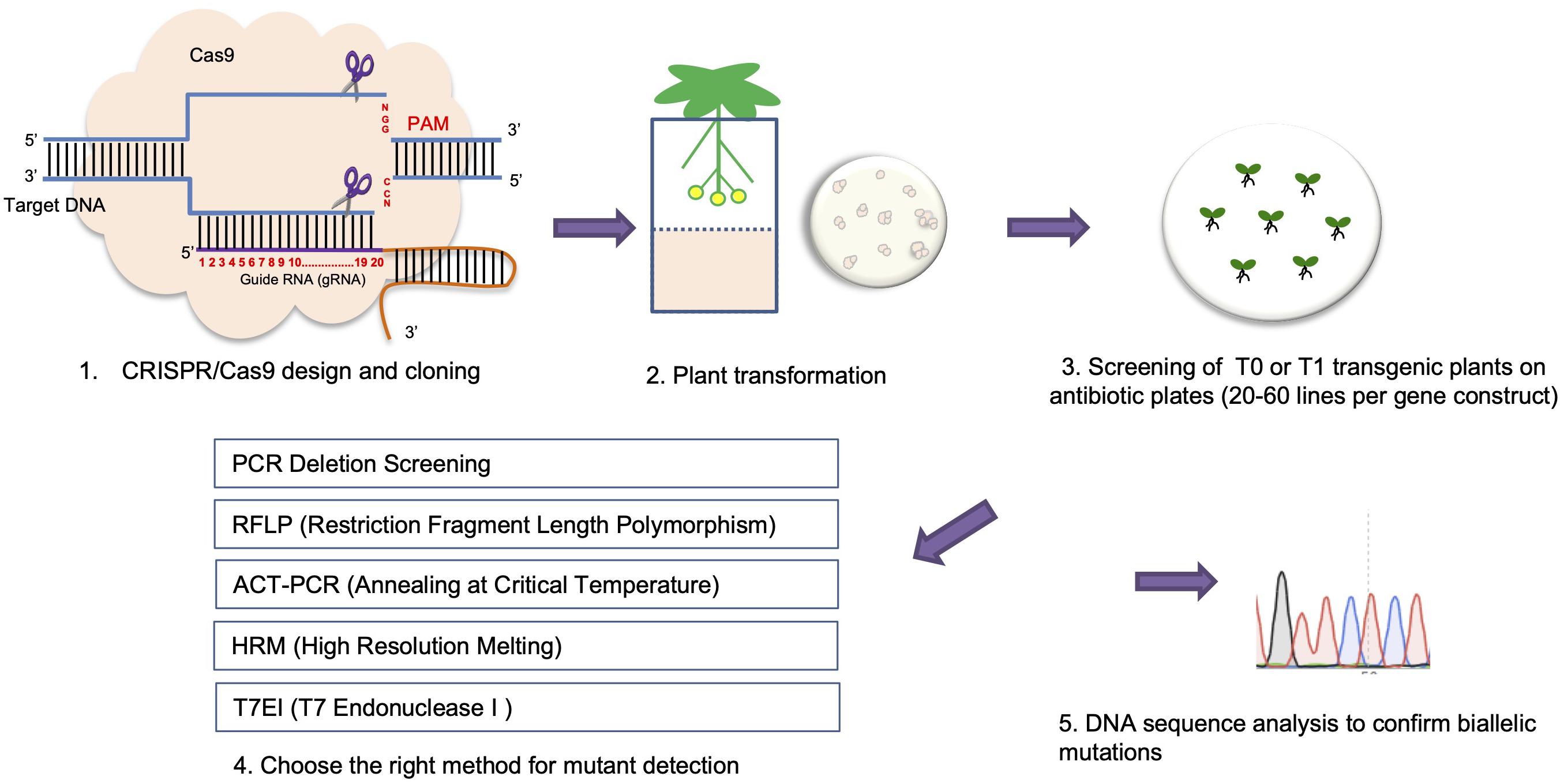



Frontiers Crispr Cas9 Genome Editing Technology A Valuable Tool For Understanding Plant Cell Wall Biosynthesis And Function Plant Science
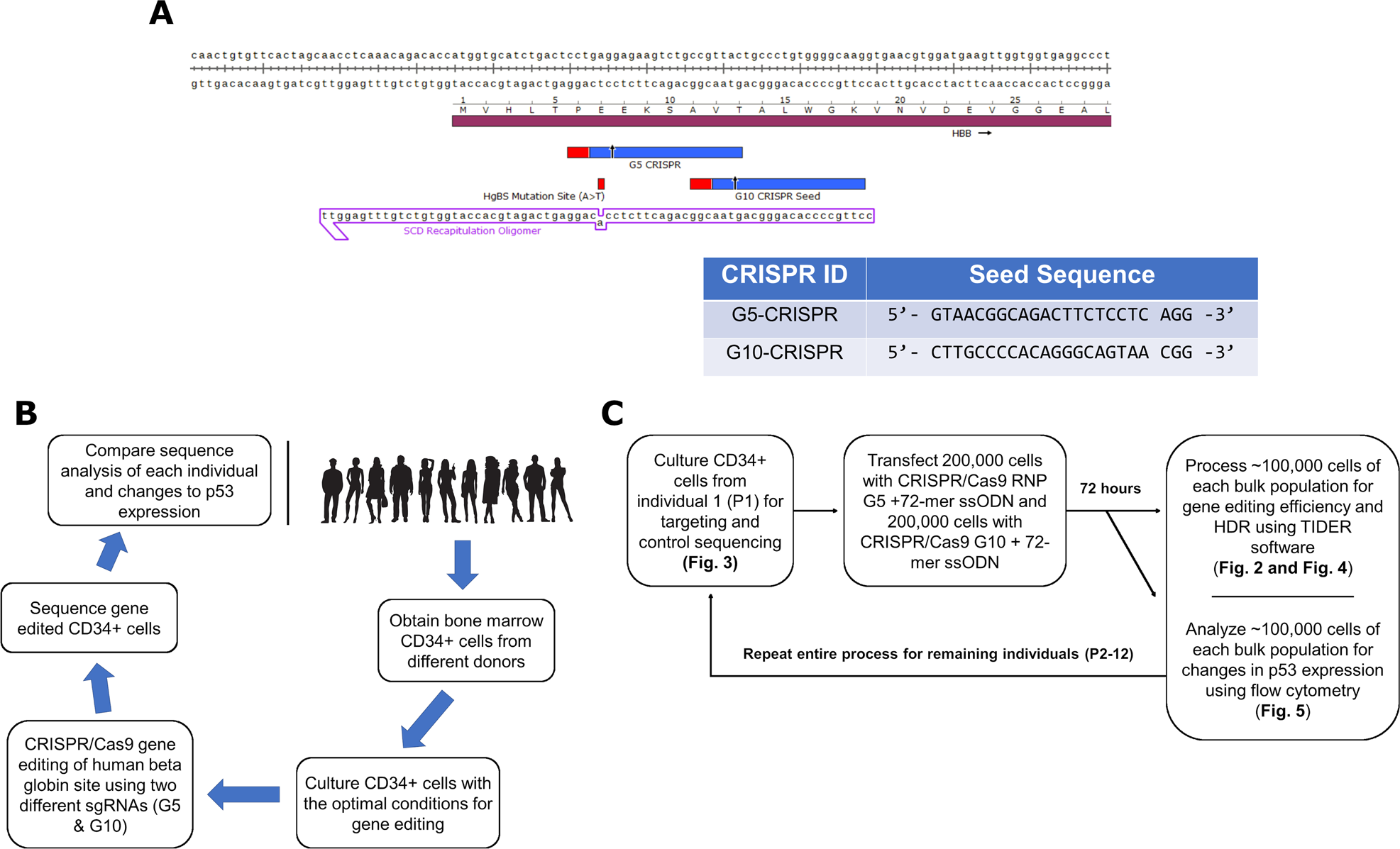



Precise And Error Prone Crispr Directed Gene Editing Activity In Human Cd34 Cells Varies Widely Among Patient Samples Gene Therapy




Type Ii Crispr Formulations Grnas Contain 4 Loop Structures Download Scientific Diagram



View Of A Streamlined Crispr Cas9 Approach For Fast Genome Editing In Toxoplasma Gondii And Besnoitia Besnoiti Journal Of Biological Methods
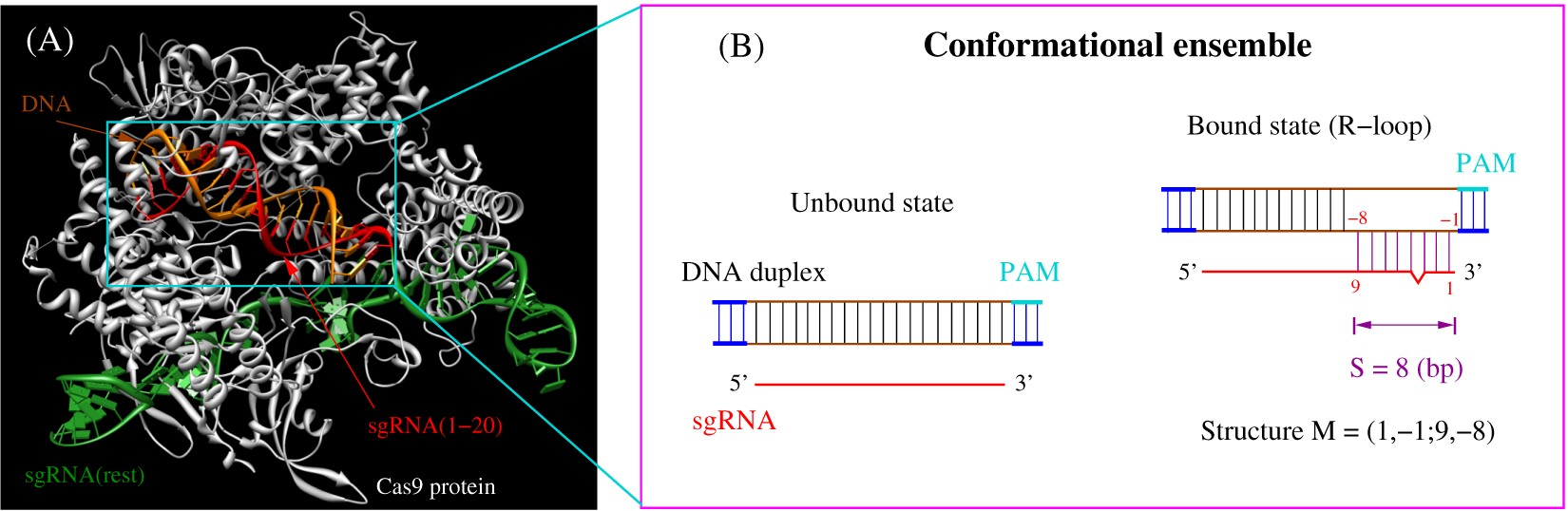



Crispr Cas9 Cleavage Efficiency Correlates Strongly With Target Sgrna Folding Stability From Physical Mechanism To Off Target Assessment Scientific Reports
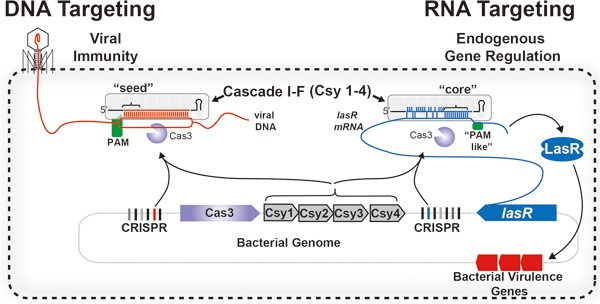



Crispr Control Of Virulence In Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Cell Research




Crispr Cas Systems In Genome Editing Methodologies And Tools For Sgrna Design Off Target Evaluation And Strategies To Mitigate Off Target Effects Manghwar Advanced Science Wiley Online Library



Team Cu Boulder Project Modeling 14 Igem Org



Crispr Cas
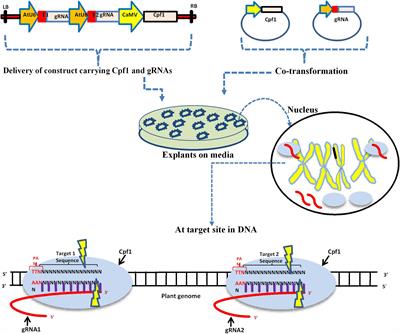



Frontiers The Rise Of The Crispr Cpf1 System For Efficient Genome Editing In Plants Plant Science




Computational Approaches For Effective Crispr Guide Rna Design And Evaluation Sciencedirect
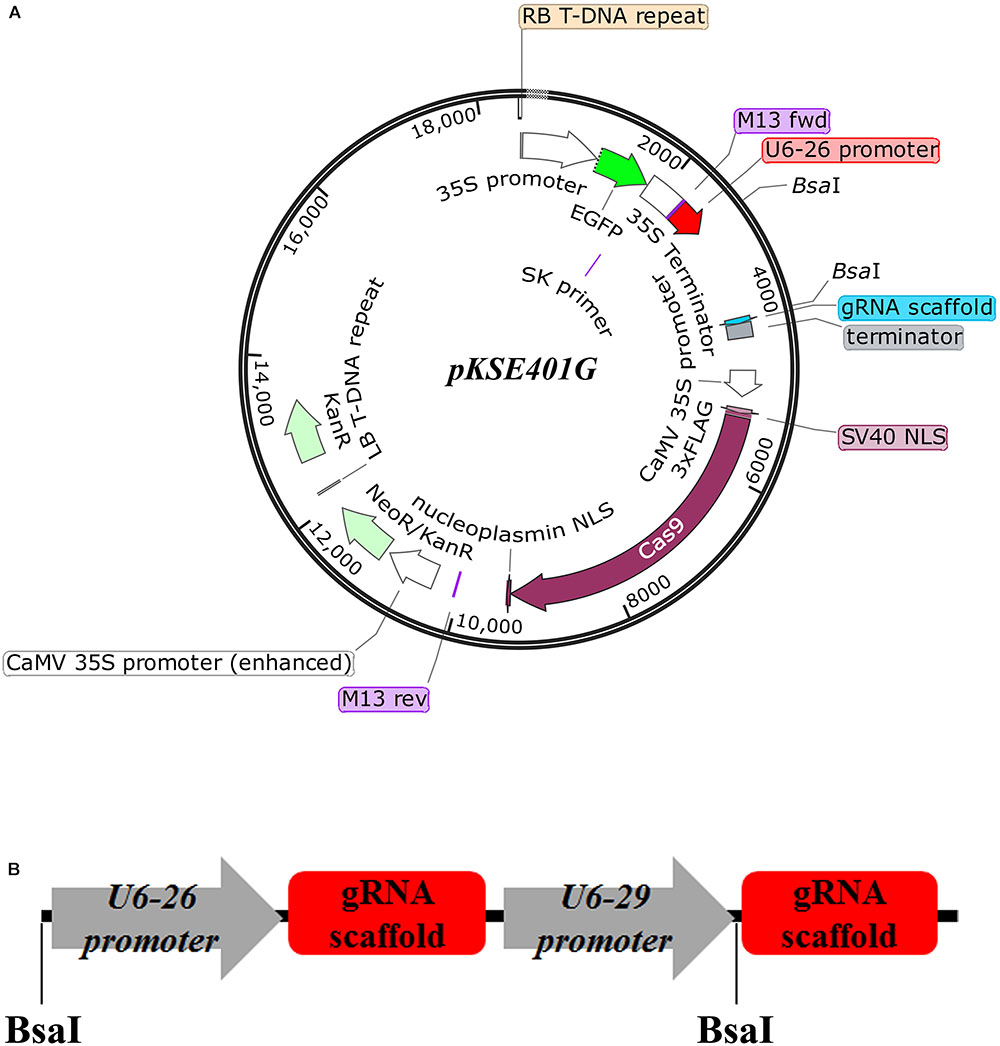



Frontiers Development And Validation Of An Effective Crispr Cas9 Vector For Efficiently Isolating Positive Transformants And Transgene Free Mutants In A Wide Range Of Plant Species Plant Science




Crispr Cas System Recent Advances And Future Prospects For Genome Editing Trends In Plant Science




Figure 3 From Crispr Interference Crispri For Sequence Specific Control Of Gene Expression Semantic Scholar




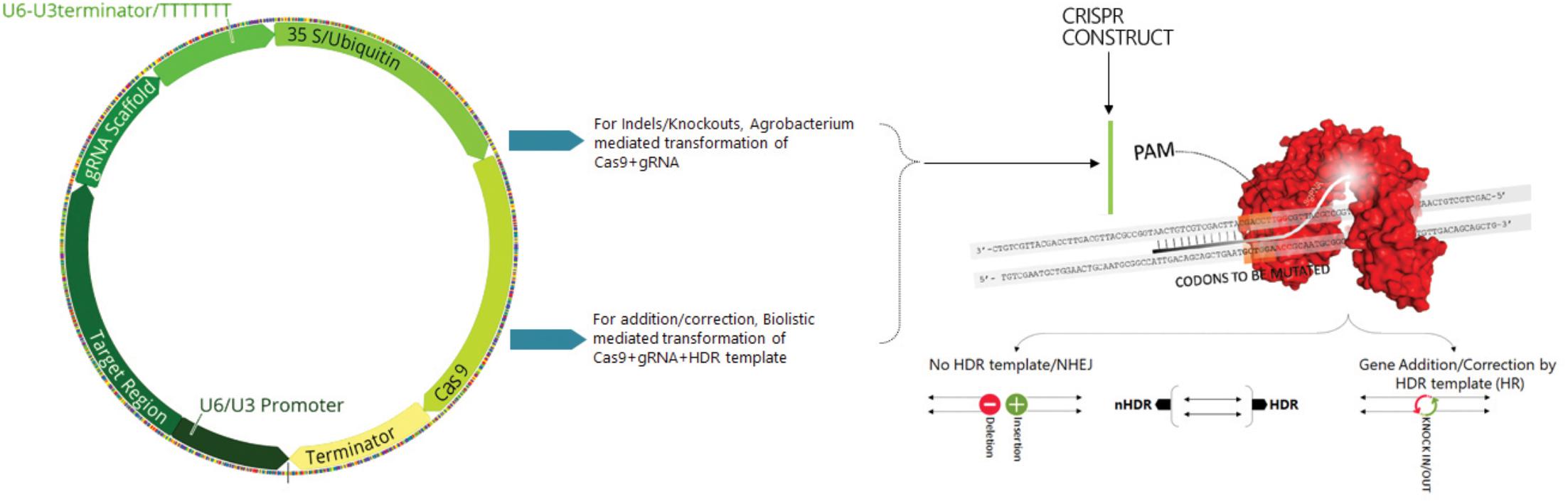
Design Principle Of A Crispr Cas9 Expression Vector For Construction Download Scientific Diagram



Crispr Rt
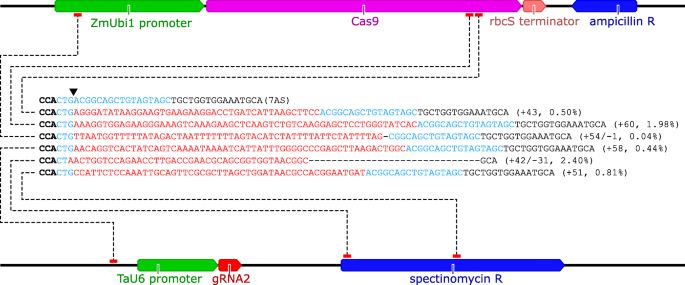



Grna Validation For Wheat Genome Editing With The Crispr Cas9 System Bmc Biotechnology Full Text




High Throughput Assay For Nicking And Cleavage By Crispr Cas Download Scientific Diagram



1



1
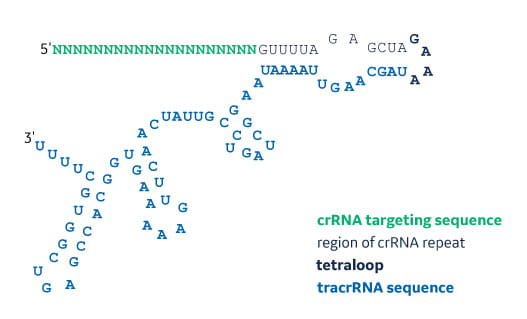



Synthetic Sgrna For Crispr Cas9 Experiments



Crispr Rt




One Or Two Mismatches In The Seed Can Be Tolerated For Crispr Activity Download Scientific Diagram




The Revolution Continues Newly Discovered Systems Expand The Crispr Cas Toolkit Sciencedirect
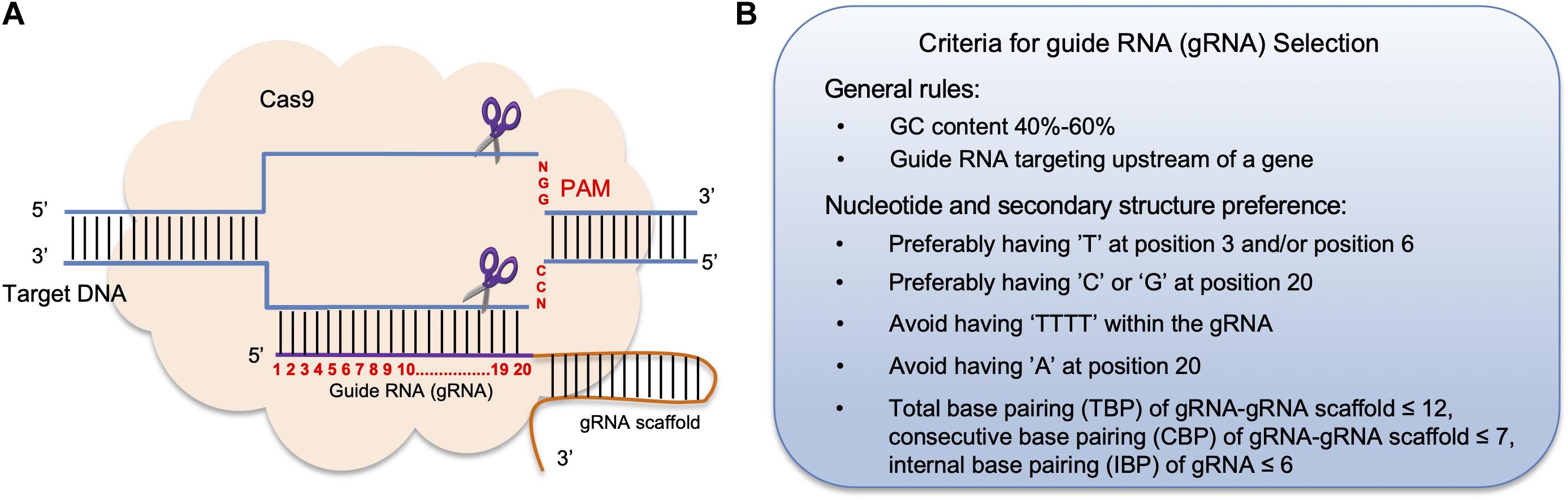



Frontiers Crispr Cas9 Genome Editing Technology A Valuable Tool For Understanding Plant Cell Wall Biosynthesis And Function Plant Science
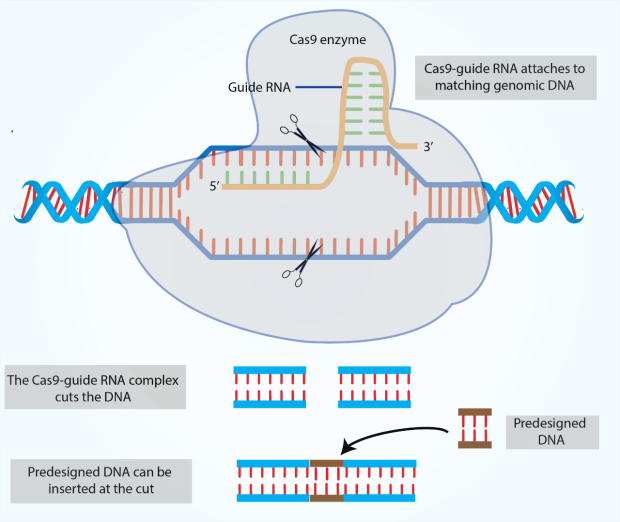



Using Crispr For Allergy And Asthma Sean N Parker Center For Allergy Asthma Research Stanford Medicine



1




Binding Of Central Seed Region In Grna Crucial For Cas13 Mediated Download Scientific Diagram




Researchers Employing Crispr For Soybean Advancement Research Highlight Soybean Research Information Network Srin
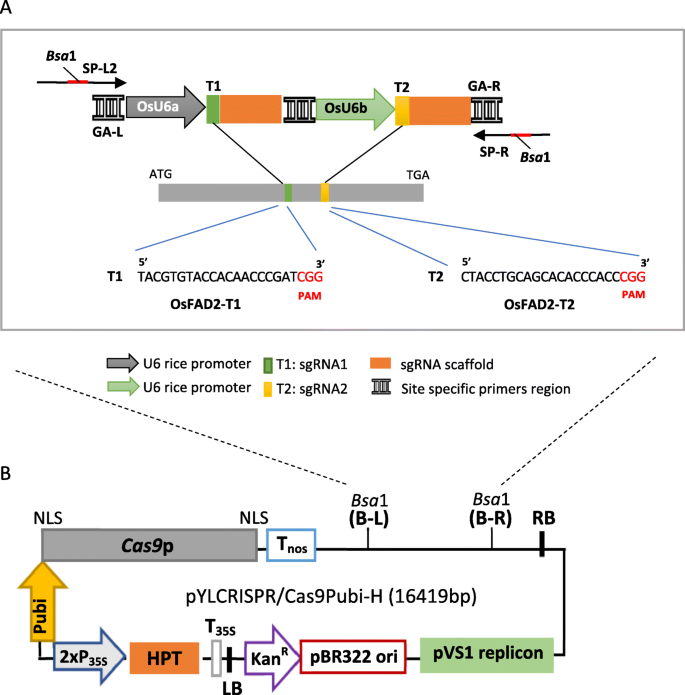



Multiplex Crispr Cas9 Mediated Genome Editing Of The Fad2 Gene In Rice A Model Genome Editing System For Oil Palm Journal Of Genetic Engineering And Biotechnology Full Text



Plos One Crispr Cas9 Mediated Phage Resistance Is Not Impeded By The Dna Modifications Of Phage T4




Determining The Specificity Of Cascade Binding Interference And Primed Adaptation In Vivo In The Escherichia Coli Type I E Crispr Cas System Mbio




Addgene Crispr Guide




The Crispr Cas9 System For Plant Genome Editing And Beyond Sciencedirect



Pnas Org



Full Article Defining The Seed Sequence Of The Cas12b Crispr Cas Effector Complex




Off Target Effects In Crispr Cas9 Mediated Genome Engineering Sciencedirect
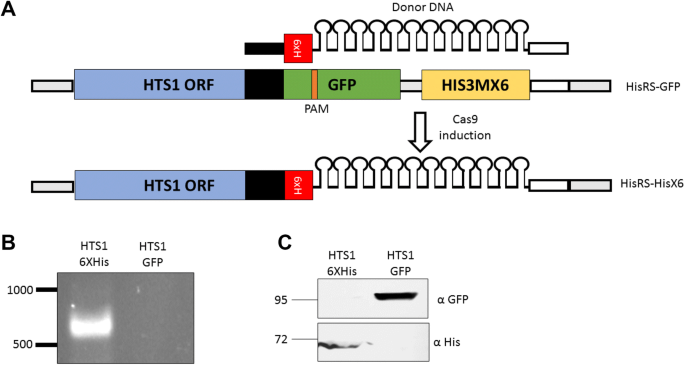



Expanding The Crispr Cas9 Toolbox For Gene Engineering In S Cerevisiae Springerlink




The Magic Cut On Target Dna By Crispr Cas9 Bioscope




Computational Approaches For Effective Crispr Guide Rna Design And Evaluation Sciencedirect




Patterns Of Crispr Cas9 Activity In Plants Animals And Microbes Bortesi 16 Plant Biotechnology Journal Wiley Online Library




Crispr Plant
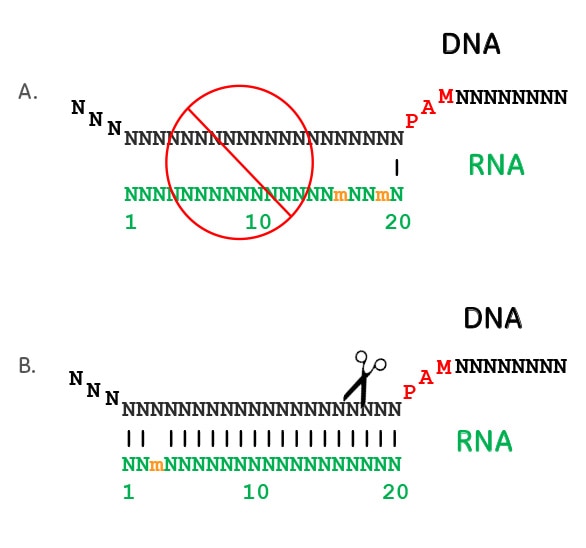



Crispr Cas9 Guide Rna Specificity




Addgene Crispr Guide




Addgene Crispr Guide




Crispr Cas12a More Precise Than Crispr Cas9
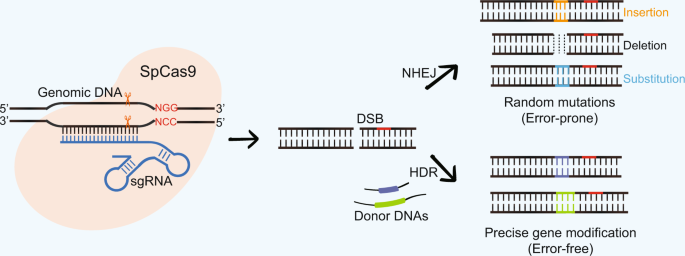



Crispr Technology Is Revolutionizing The Improvement Of Tomato And Other Fruit Crops Horticulture Research




Crispr Cas9 Abm Inc
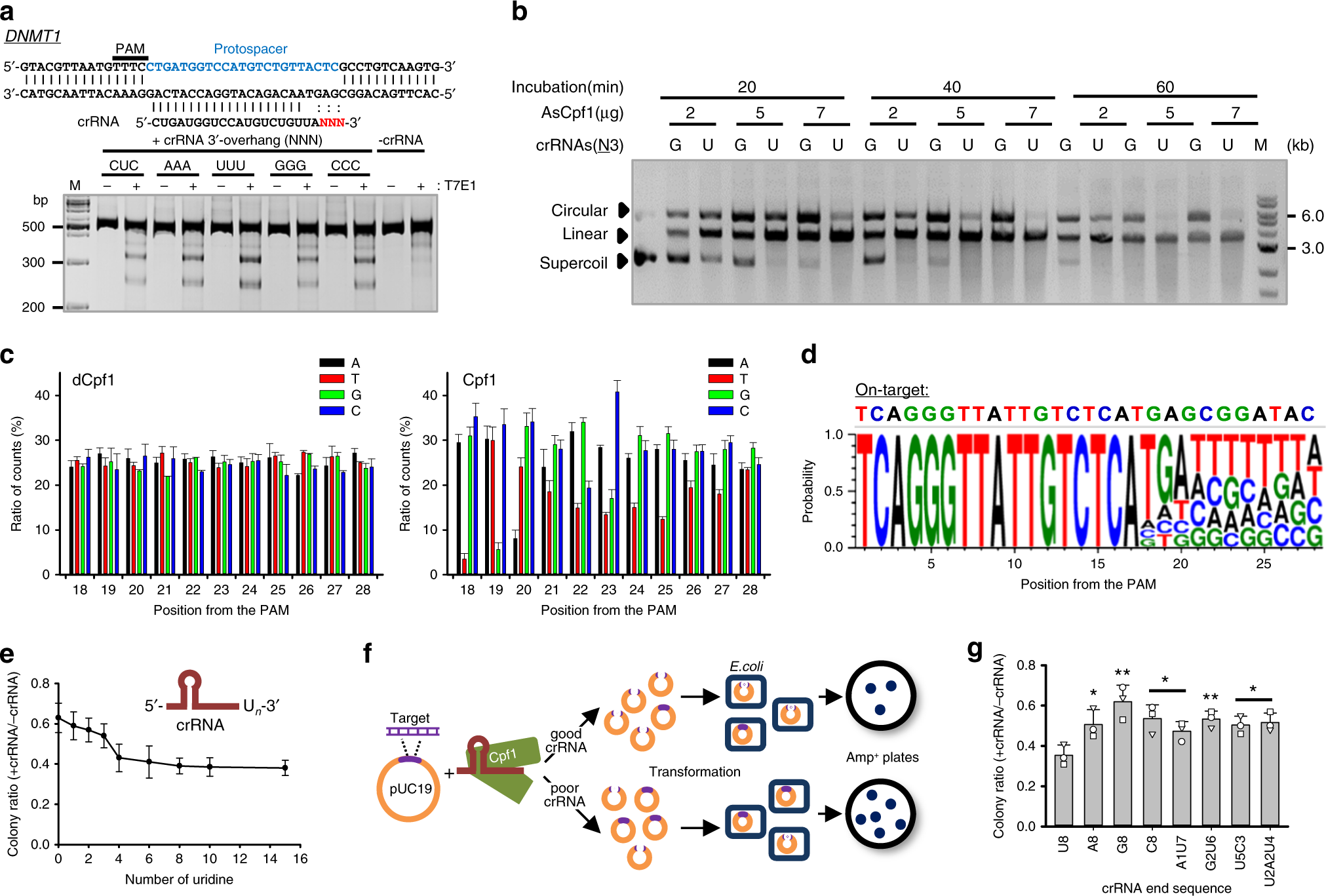



Highly Efficient Genome Editing By Crispr Cpf1 Using Crispr Rna With A Uridinylate Rich 3 Overhang Nature Communications
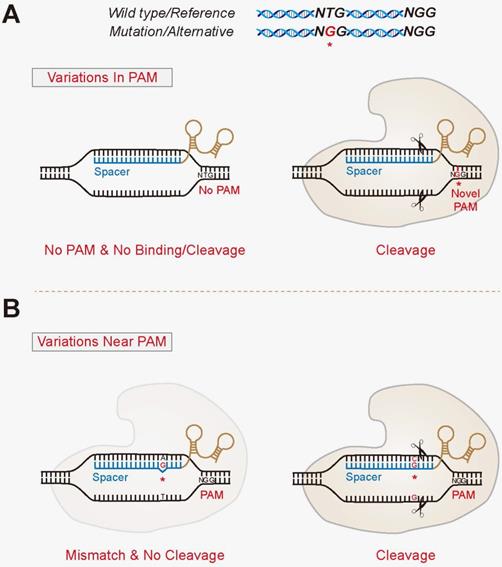



Allele Specific Genome Targeting In The Development Of Precision Medicine
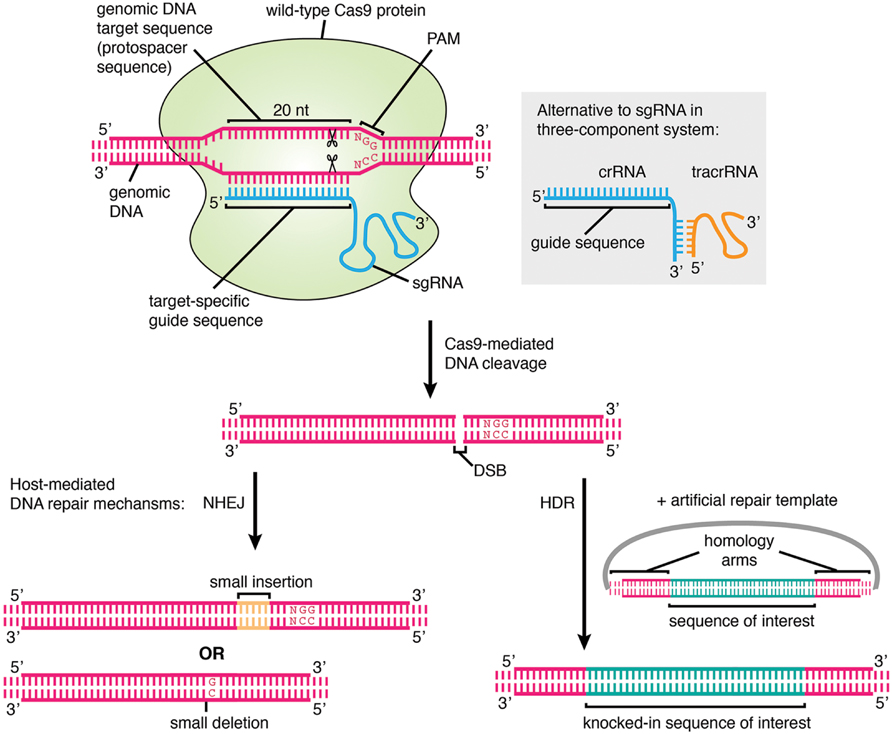



Frontiers A New Age In Functional Genomics Using Crispr Cas9 In Arrayed Library Screening Genetics
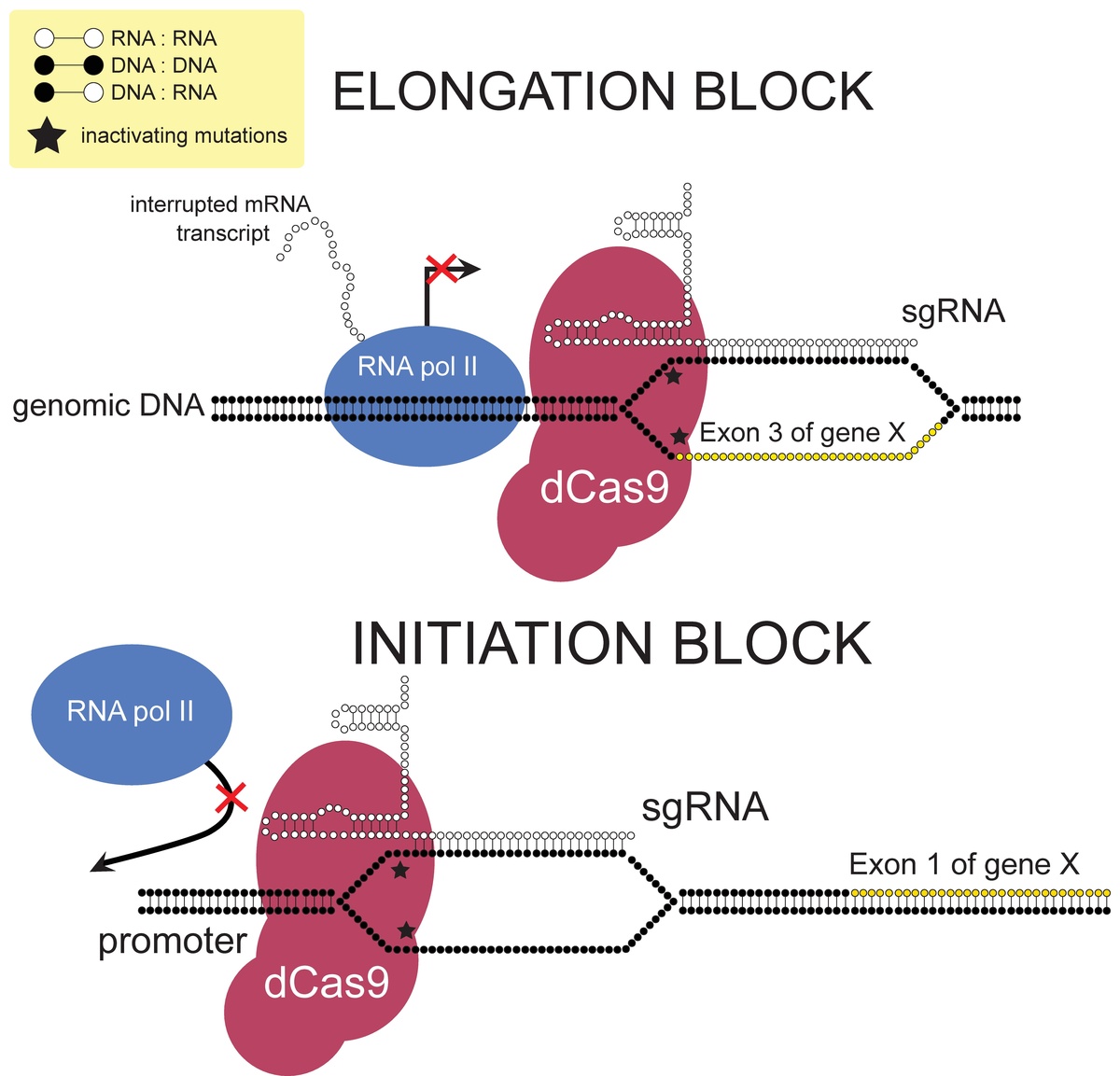



Crispr Interference Wikipedia
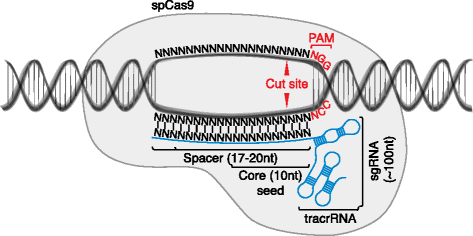



Resources For The Design Of Crispr Gene Editing Experiments Genome Biology Full Text
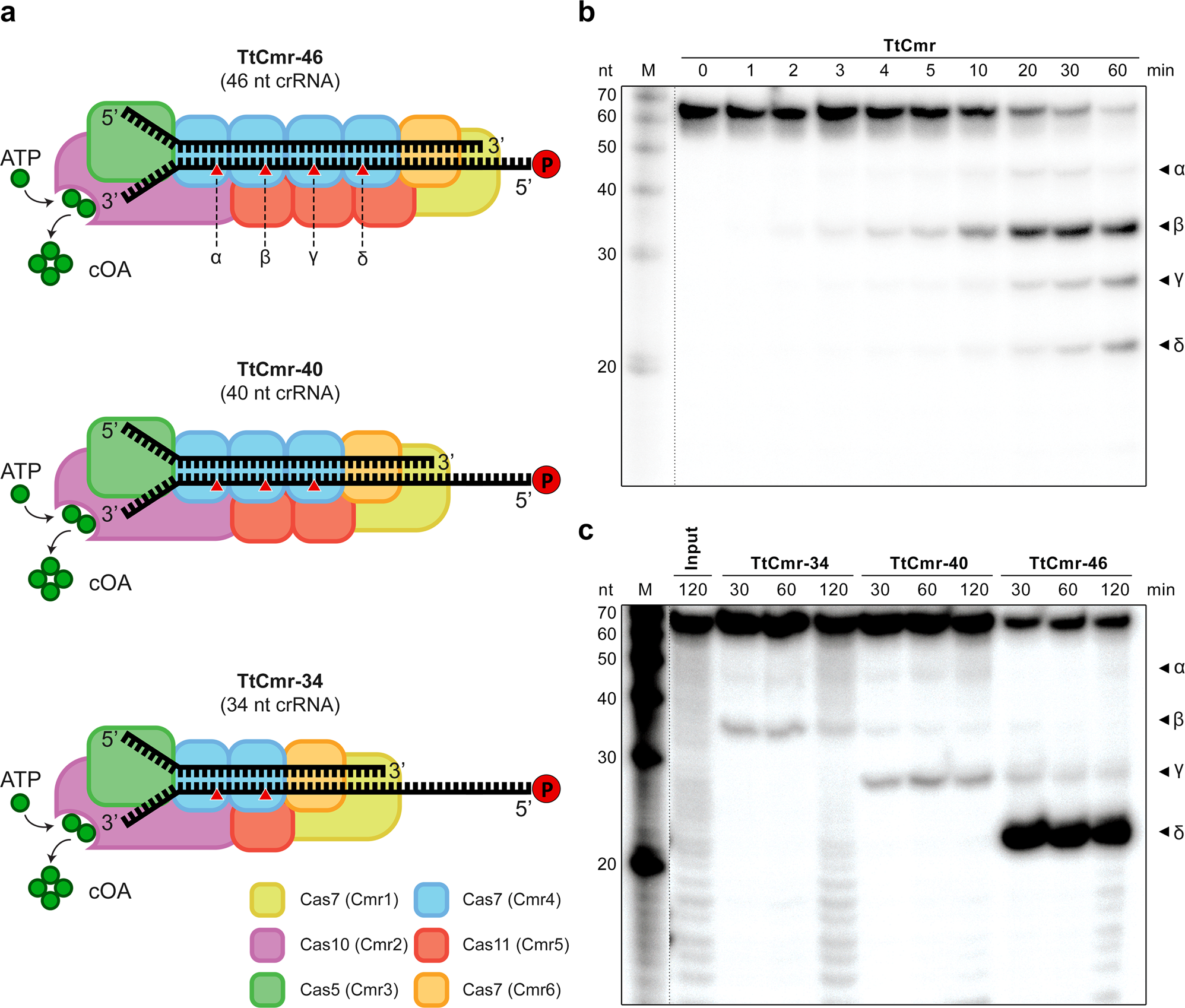



Scope Enables Type Iii Crispr Cas Diagnostics Using Flexible Targeting And Stringent Carf Ribonuclease Activation Nature Communications
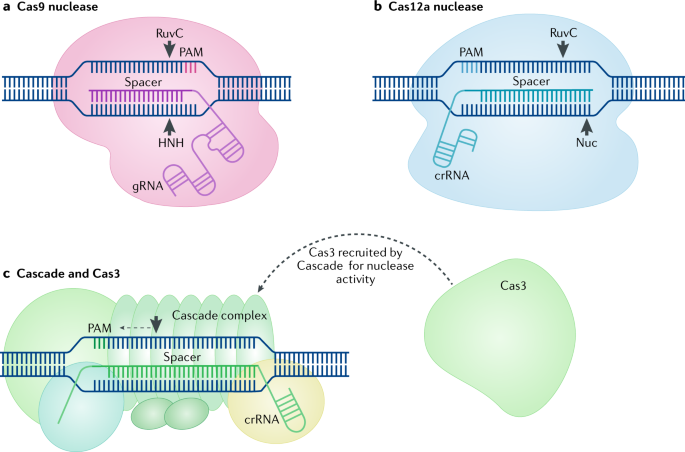



The Next Generation Of Crispr Cas Technologies And Applications




Efficient Multiplex Biallelic Zebrafish Genome Editing Using A Crispr Nuclease System Pnas




Addgene Crispr Guide
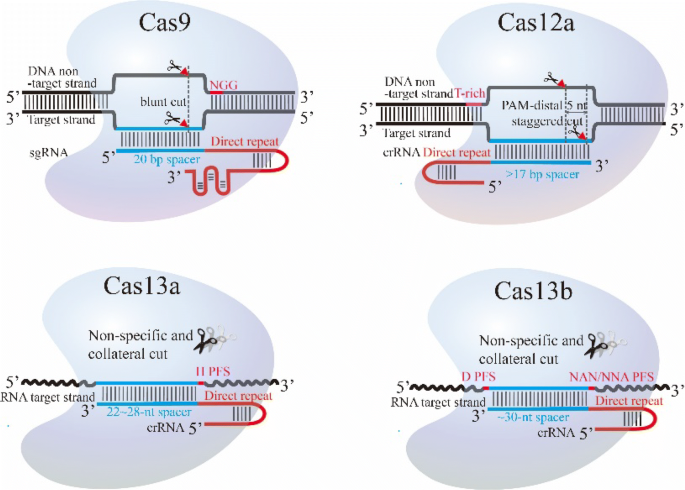



Class 2 Crispr Cas An Expanding Biotechnology Toolbox For And Beyond Genome Editing Cell Bioscience Full Text
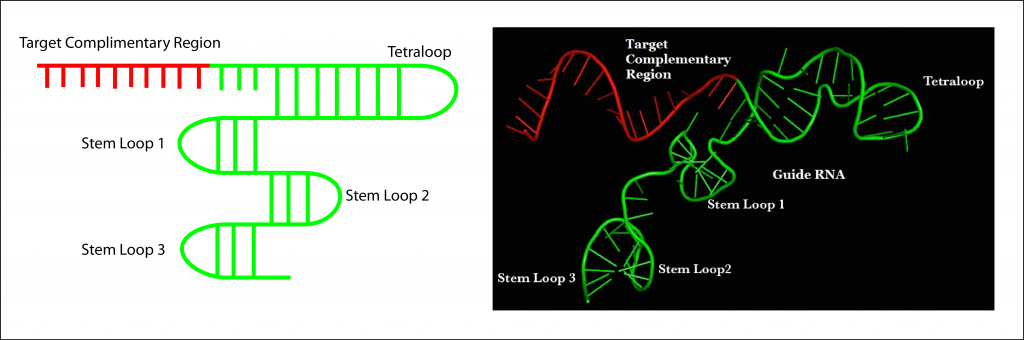



Cas9 Mechanism Crispr Cas9




Off Switch During Error Prone Cell Cycle Phase May Fix Crispr S Unwanted Changes Problem Seed World




Schematic Illustration Of The Crispr Cas9 System Structure And The Download Scientific Diagram



1




Addgene Crispr Guide
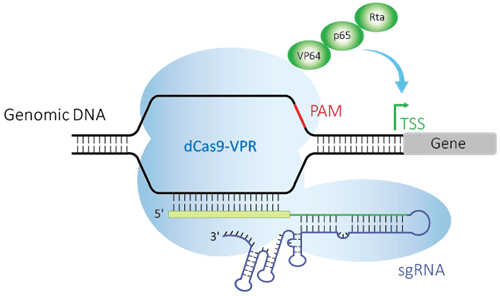



Crispr Activation




Efficient Crispr Cas9 Mediated Biallelic Gene Disruption And Site Specific Knockin After Rapid Selection Of Highly Active Sgrnas In Pigs Scientific Reports
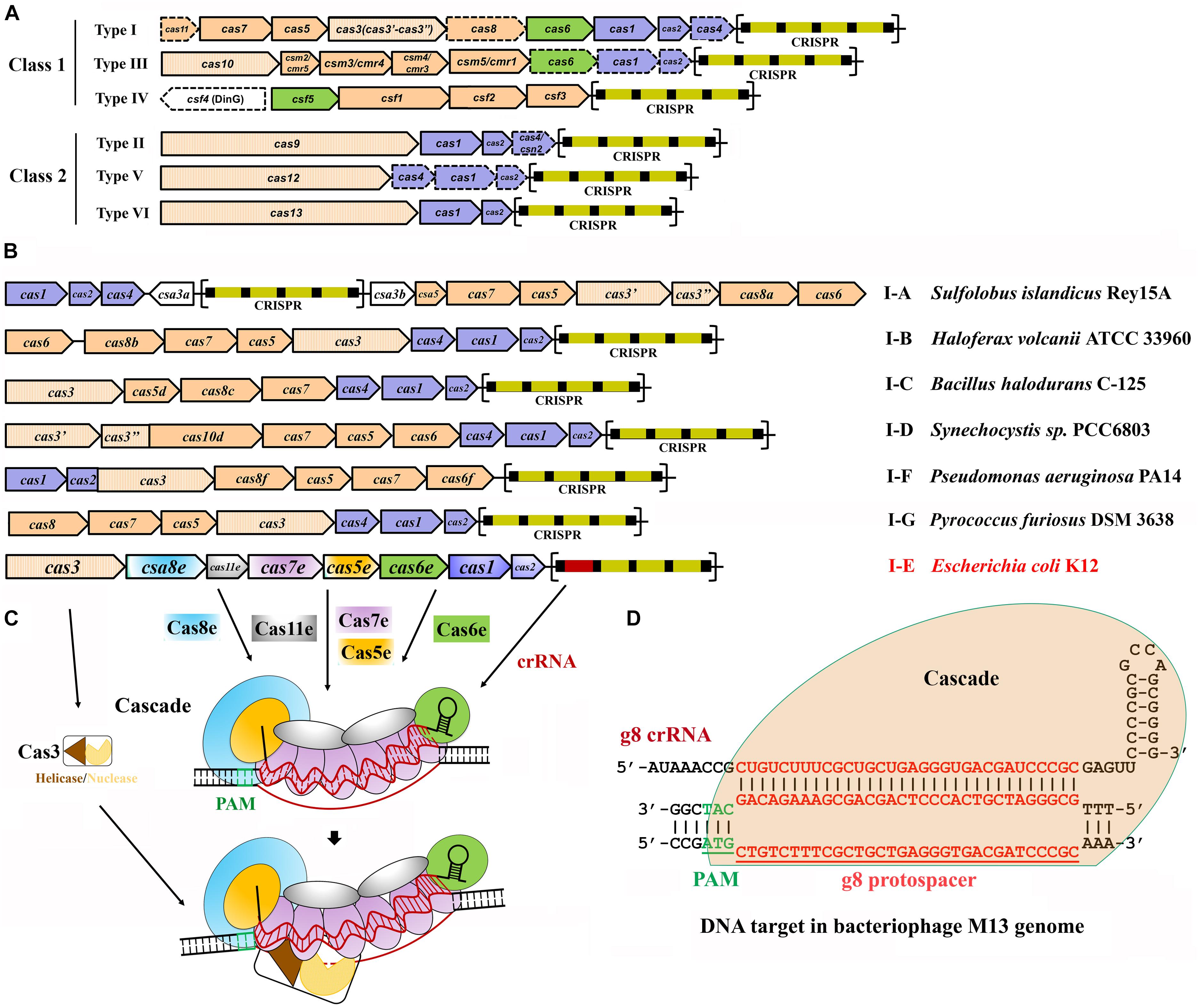



Frontiers Endogenous Type I Crispr Cas From Foreign Dna Defense To Prokaryotic Engineering Bioengineering And Biotechnology




C2c2 Is A Single Component Programmable Rna Guided Rna Targeting Crispr Effector



Cell Com




Crispr Cas Systems In Genome Editing Methodologies And Tools For Sgrna Design Off Target Evaluation And Strategies To Mitigate Off Target Effects Manghwar Advanced Science Wiley Online Library
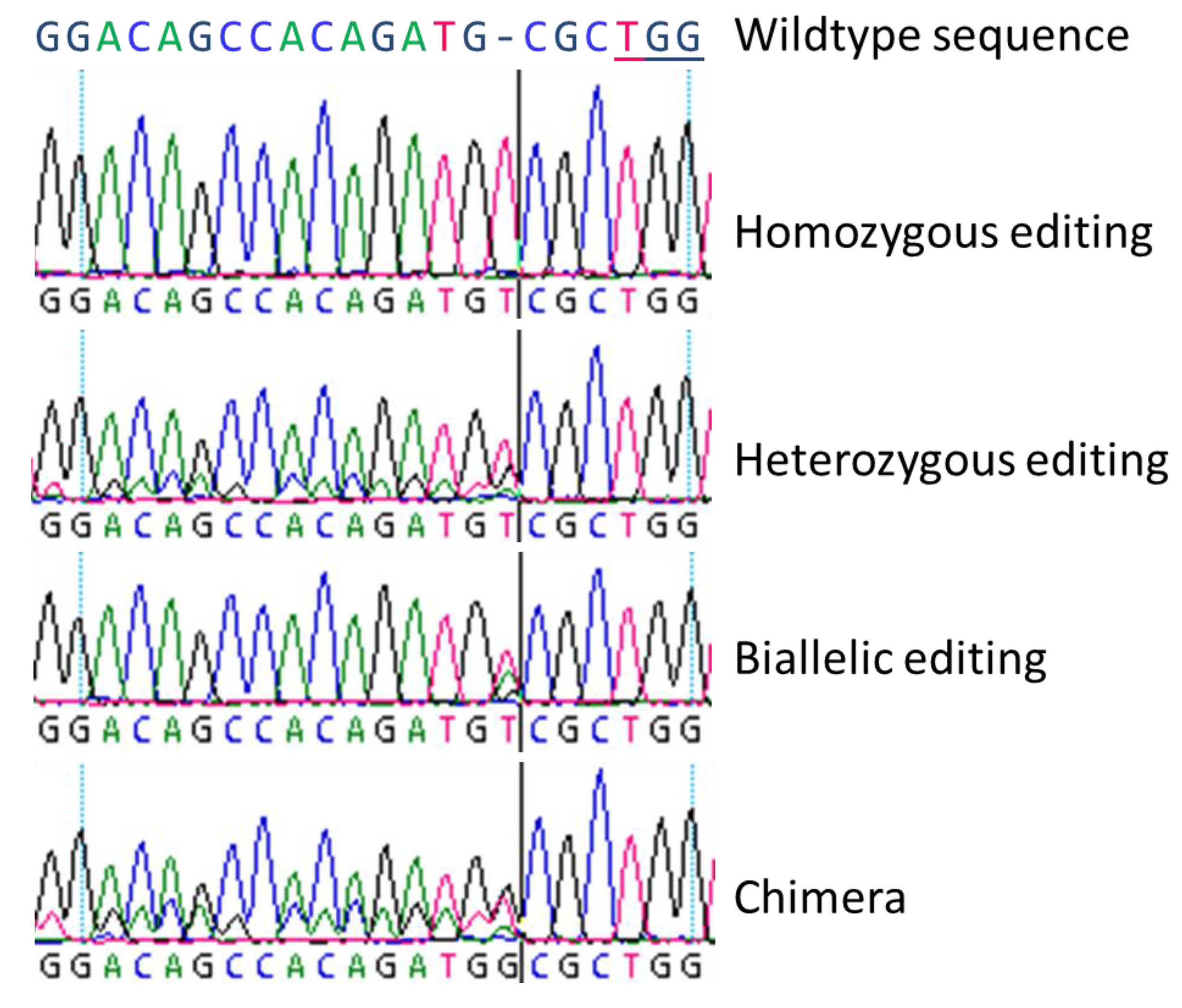



Ijms Free Full Text Evaluating The Efficiency Of Grnas In Crispr Cas9 Mediated Genome Editing In Poplars Html
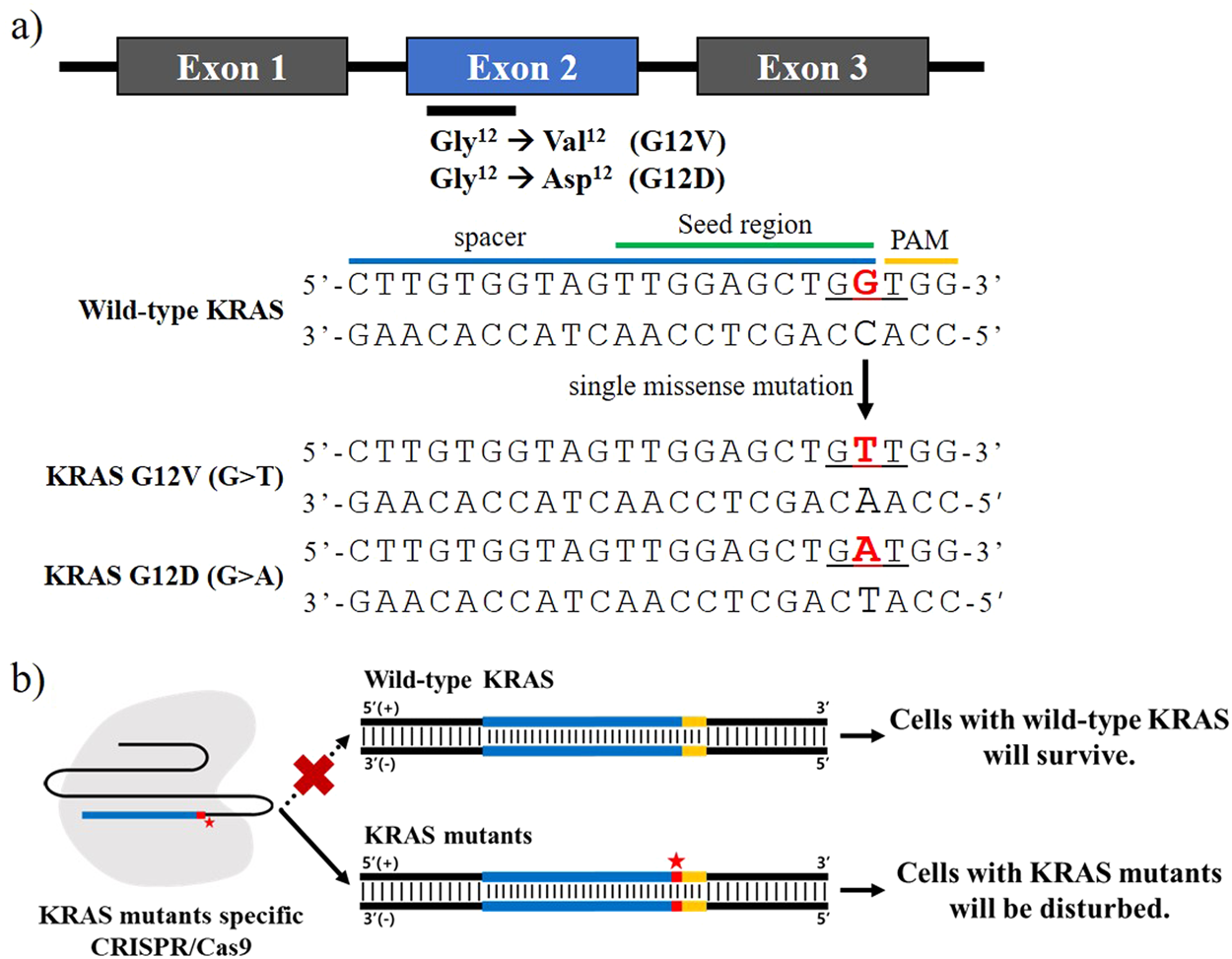



Selective Targeting Of Kras Oncogenic Alleles By Crispr Cas9 Inhibits Proliferation Of Cancer Cells Scientific Reports
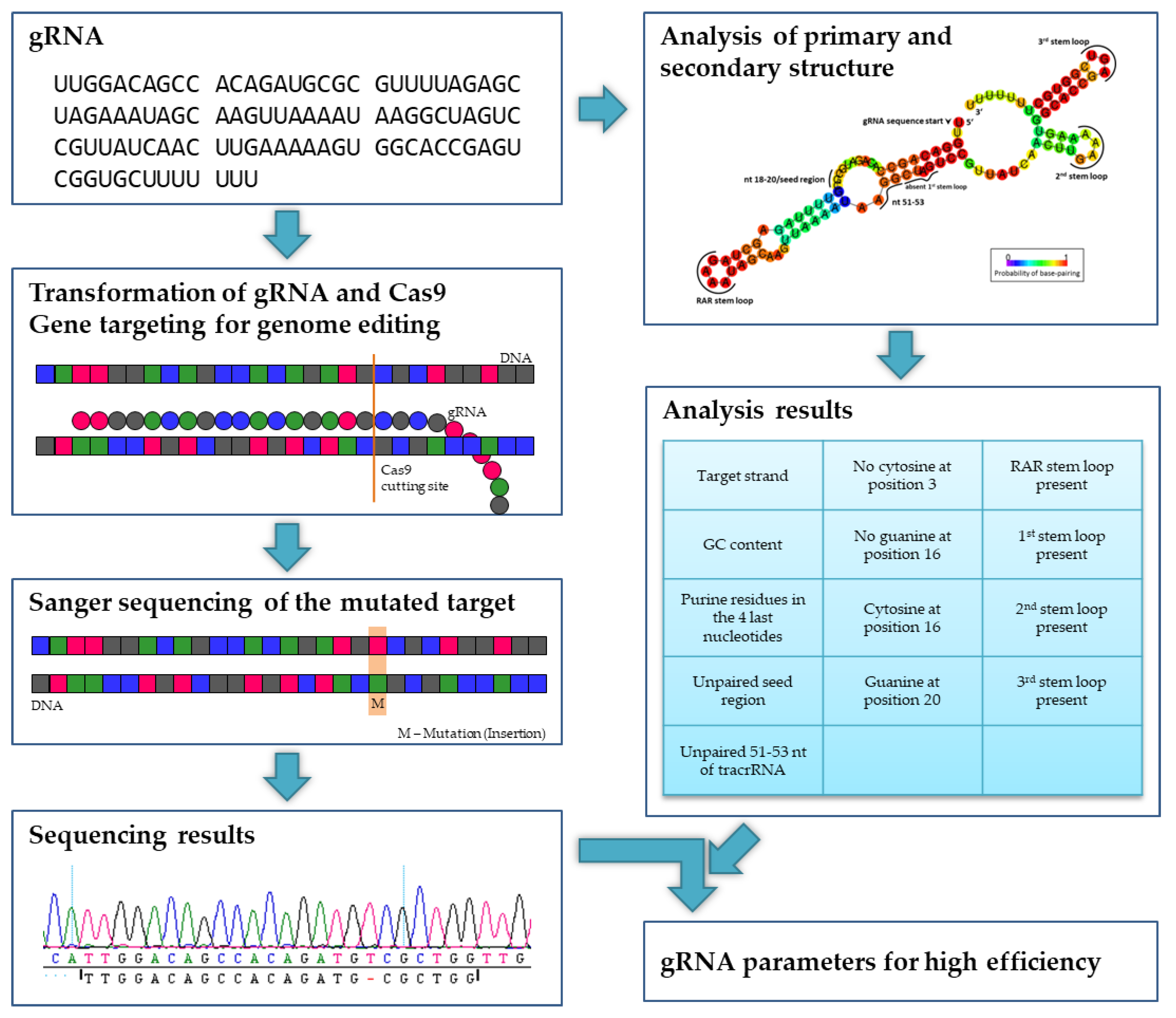



Ijms Free Full Text Evaluating The Efficiency Of Grnas In Crispr Cas9 Mediated Genome Editing In Poplars Html
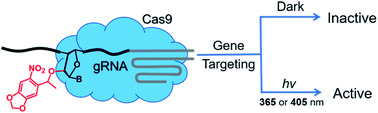



Photocontrol Of Crispr Cas9 Function By Site Specific Chemical Modification Of Guide Rna Chemical Science Rsc Publishing
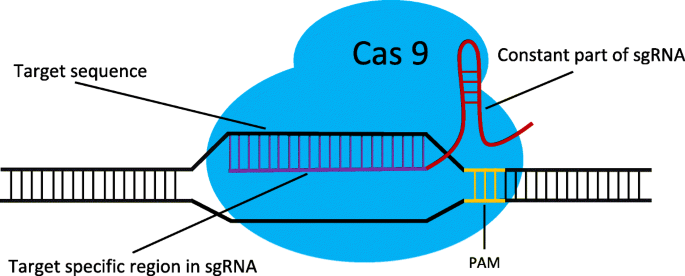



Offscan A Universal And Fast Crispr Off Target Sites Detection Tool Bmc Genomics Full Text



Overview Of Crispr Cas9 Systems Duke Viral Vector Core




Off Target Genome Editing Wikipedia



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿